Demonstrate how to generate and display a Voroni diagram.

A Voronoi diagram is a diagram consisting of a number of sites. Each Voronoi site "s" also has a Voronoi cell consisting of all points closest to "s".
See algorithm K-means++ clustering.
C
C code drawing a color map of a set of Voronoi sites.
Image is in PNM P6, written to stdout.
Run as a.out > stuff.pnm.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N_SITES 150
double site[N_SITES][2];
unsigned char rgb[N_SITES][3];
int size_x = 640, size_y = 480;
inline double sq2(double x, double y)
{
return x * x + y * y;
}
#define for_k for (k = 0; k < N_SITES; k++)
int nearest_site(double x, double y)
{
int k, ret = 0;
double d, dist = 0;
for_k {
d = sq2(x - site[k][0], y - site[k][1]);
if (!k || d < dist) {
dist = d, ret = k;
}
}
return ret;
}
/* see if a pixel is different from any neighboring ones */
int at_edge(int *color, int y, int x)
{
int i, j, c = color[y * size_x + x];
for (i = y - 1; i <= y + 1; i++) {
if (i < 0 || i >= size_y) continue;
for (j = x - 1; j <= x + 1; j++) {
if (j < 0 || j >= size_x) continue;
if (color[i * size_x + j] != c) return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
#define AA_RES 4 /* average over 4x4 supersampling grid */
void aa_color(unsigned char *pix, int y, int x)
{
int i, j, n;
double r = 0, g = 0, b = 0, xx, yy;
for (i = 0; i < AA_RES; i++) {
yy = y + 1. / AA_RES * i + .5;
for (j = 0; j < AA_RES; j++) {
xx = x + 1. / AA_RES * j + .5;
n = nearest_site(xx, yy);
r += rgb[n][0];
g += rgb[n][1];
b += rgb[n][2];
}
}
pix[0] = r / (AA_RES * AA_RES);
pix[1] = g / (AA_RES * AA_RES);
pix[2] = b / (AA_RES * AA_RES);
}
#define for_i for (i = 0; i < size_y; i++)
#define for_j for (j = 0; j < size_x; j++)
void gen_map()
{
int i, j, k;
int *nearest = malloc(sizeof(int) * size_y * size_x);
unsigned char *ptr, *buf, color;
ptr = buf = malloc(3 * size_x * size_y);
for_i for_j nearest[i * size_x + j] = nearest_site(j, i);
for_i for_j {
if (!at_edge(nearest, i, j))
memcpy(ptr, rgb[nearest[i * size_x + j]], 3);
else /* at edge, do anti-alias rastering */
aa_color(ptr, i, j);
ptr += 3;
}
/* draw sites */
for (k = 0; k < N_SITES; k++) {
color = (rgb[k][0]*.25 + rgb[k][1]*.6 + rgb[k][2]*.15 > 80) ? 0 : 255;
for (i = site[k][1] - 1; i <= site[k][1] + 1; i++) {
if (i < 0 || i >= size_y) continue;
for (j = site[k][0] - 1; j <= site[k][0] + 1; j++) {
if (j < 0 || j >= size_x) continue;
ptr = buf + 3 * (i * size_x + j);
ptr[0] = ptr[1] = ptr[2] = color;
}
}
}
printf("P6\n%d %d\n255\n", size_x, size_y);
fflush(stdout);
fwrite(buf, size_y * size_x * 3, 1, stdout);
}
#define frand(x) (rand() / (1. + RAND_MAX) * x)
int main()
{
int k;
for_k {
site[k][0] = frand(size_x);
site[k][1] = frand(size_y);
rgb [k][0] = frand(256);
rgb [k][1] = frand(256);
rgb [k][2] = frand(256);
}
gen_map();
return 0;
}
C++
#include <windows.h>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class MyBitmap {
public:
MyBitmap() : pen_(nullptr) {}
~MyBitmap() {
DeleteObject(pen_);
DeleteDC(hdc_);
DeleteObject(bmp_);
}
bool Create(int w, int h) {
BITMAPINFO bi;
ZeroMemory(&bi, sizeof(bi));
bi.bmiHeader.biSize = sizeof(bi.bmiHeader);
bi.bmiHeader.biBitCount = sizeof(DWORD) * 8;
bi.bmiHeader.biCompression = BI_RGB;
bi.bmiHeader.biPlanes = 1;
bi.bmiHeader.biWidth = w;
bi.bmiHeader.biHeight = -h;
void *bits_ptr = nullptr;
HDC dc = GetDC(GetConsoleWindow());
bmp_ = CreateDIBSection(dc, &bi, DIB_RGB_COLORS, &bits_ptr, nullptr, 0);
if (!bmp_) return false;
hdc_ = CreateCompatibleDC(dc);
SelectObject(hdc_, bmp_);
ReleaseDC(GetConsoleWindow(), dc);
width_ = w;
height_ = h;
return true;
}
void SetPenColor(DWORD clr) {
if (pen_) DeleteObject(pen_);
pen_ = CreatePen(PS_SOLID, 1, clr);
SelectObject(hdc_, pen_);
}
bool SaveBitmap(const char* path) {
HANDLE file = CreateFile(path, GENERIC_WRITE, 0, nullptr, CREATE_ALWAYS, FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, nullptr);
if (file == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) {
return false;
}
BITMAPFILEHEADER fileheader;
BITMAPINFO infoheader;
BITMAP bitmap;
GetObject(bmp_, sizeof(bitmap), &bitmap);
DWORD* dwp_bits = new DWORD[bitmap.bmWidth * bitmap.bmHeight];
ZeroMemory(dwp_bits, bitmap.bmWidth * bitmap.bmHeight * sizeof(DWORD));
ZeroMemory(&infoheader, sizeof(BITMAPINFO));
ZeroMemory(&fileheader, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER));
infoheader.bmiHeader.biBitCount = sizeof(DWORD) * 8;
infoheader.bmiHeader.biCompression = BI_RGB;
infoheader.bmiHeader.biPlanes = 1;
infoheader.bmiHeader.biSize = sizeof(infoheader.bmiHeader);
infoheader.bmiHeader.biHeight = bitmap.bmHeight;
infoheader.bmiHeader.biWidth = bitmap.bmWidth;
infoheader.bmiHeader.biSizeImage = bitmap.bmWidth * bitmap.bmHeight * sizeof(DWORD);
fileheader.bfType = 0x4D42;
fileheader.bfOffBits = sizeof(infoheader.bmiHeader) + sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER);
fileheader.bfSize = fileheader.bfOffBits + infoheader.bmiHeader.biSizeImage;
GetDIBits(hdc_, bmp_, 0, height_, (LPVOID)dwp_bits, &infoheader, DIB_RGB_COLORS);
DWORD wb;
WriteFile(file, &fileheader, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), &wb, nullptr);
WriteFile(file, &infoheader.bmiHeader, sizeof(infoheader.bmiHeader), &wb, nullptr);
WriteFile(file, dwp_bits, bitmap.bmWidth * bitmap.bmHeight * 4, &wb, nullptr);
CloseHandle(file);
delete[] dwp_bits;
return true;
}
HDC hdc() { return hdc_; }
int width() { return width_; }
int height() { return height_; }
private:
HBITMAP bmp_;
HDC hdc_;
HPEN pen_;
int width_, height_;
};
static int DistanceSqrd(const Point& point, int x, int y) {
int xd = x - point.x;
int yd = y - point.y;
return (xd * xd) + (yd * yd);
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class Voronoi {
public:
void Make(MyBitmap* bmp, int count) {
bmp_ = bmp;
CreatePoints(count);
CreateColors();
CreateSites();
SetSitesPoints();
}
private:
void CreateSites() {
int w = bmp_->width(), h = bmp_->height(), d;
for (int hh = 0; hh < h; hh++) {
for (int ww = 0; ww < w; ww++) {
int ind = -1, dist = INT_MAX;
for (size_t it = 0; it < points_.size(); it++) {
const Point& p = points_[it];
d = DistanceSqrd(p, ww, hh);
if (d < dist) {
dist = d;
ind = it;
}
}
if (ind > -1)
SetPixel(bmp_->hdc(), ww, hh, colors_[ind]);
else
__asm nop // should never happen!
}
}
}
void SetSitesPoints() {
for (const auto& point : points_) {
int x = point.x, y = point.y;
for (int i = -1; i < 2; i++)
for (int j = -1; j < 2; j++)
SetPixel(bmp_->hdc(), x + i, y + j, 0);
}
}
void CreatePoints(int count) {
const int w = bmp_->width() - 20, h = bmp_->height() - 20;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
points_.push_back({ rand() % w + 10, rand() % h + 10 });
}
}
void CreateColors() {
for (size_t i = 0; i < points_.size(); i++) {
DWORD c = RGB(rand() % 200 + 50, rand() % 200 + 55, rand() % 200 + 50);
colors_.push_back(c);
}
}
vector<Point> points_;
vector<DWORD> colors_;
MyBitmap* bmp_;
};
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
ShowWindow(GetConsoleWindow(), SW_MAXIMIZE);
srand(GetTickCount());
MyBitmap bmp;
bmp.Create(512, 512);
bmp.SetPenColor(0);
Voronoi v;
v.Make(&bmp, 50);
BitBlt(GetDC(GetConsoleWindow()), 20, 20, 512, 512, bmp.hdc(), 0, 0, SRCCOPY);
bmp.SaveBitmap("v.bmp");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
D
Translated from Go.
import std.random, std.algorithm, std.range, bitmap;
struct Point { uint x, y; }
enum randomPoints = (in size_t nPoints, in size_t nx, in size_t ny) =>
nPoints.iota
.map!((int) => Point(uniform(0, nx), uniform(0, ny)))
.array;
Image!RGB generateVoronoi(in Point[] pts,
in size_t nx, in size_t ny) /*nothrow*/ {
// Generate a random color for each centroid.
immutable rndRBG = (int) => RGB(uniform!"[]"(ubyte.min, ubyte.max),
uniform!"[]"(ubyte.min, ubyte.max),
uniform!"[]"(ubyte.min, ubyte.max));
const colors = pts.length.iota.map!rndRBG.array;
// Generate diagram by coloring pixels with color of nearest site.
auto img = new typeof(return)(nx, ny);
foreach (immutable x; 0 .. nx)
foreach (immutable y; 0 .. ny) {
immutable dCmp = (in Point a, in Point b) pure nothrow =>
((a.x - x) ^^ 2 + (a.y - y) ^^ 2) <
((b.x - x) ^^ 2 + (b.y - y) ^^ 2);
// img[x, y] = colors[pts.reduce!(min!dCmp)];
img[x, y] = colors[pts.length - pts.minPos!dCmp.length];
}
// Mark each centroid with a white dot.
foreach (immutable p; pts)
img[p.tupleof] = RGB.white;
return img;
}
void main() {
enum imageWidth = 640,
imageHeight = 480;
randomPoints(150, imageWidth, imageHeight)
.generateVoronoi(imageWidth, imageHeight)
.savePPM6("voronoi.ppm");
}
Go

package main
import (
"fmt"
"image"
"image/color"
"image/draw"
"image/png"
"math/rand"
"os"
"time"
)
const (
imageWidth = 300
imageHeight = 200
nSites = 10
)
func main() {
writePngFile(generateVoronoi(randomSites()))
}
func generateVoronoi(sx, sy []int) image.Image {
// generate a random color for each site
sc := make([]color.NRGBA, nSites)
for i := range sx {
sc[i] = color.NRGBA{uint8(rand.Intn(256)), uint8(rand.Intn(256)),
uint8(rand.Intn(256)), 255}
}
// generate diagram by coloring each pixel with color of nearest site
img := image.NewNRGBA(image.Rect(0, 0, imageWidth, imageHeight))
for x := 0; x < imageWidth; x++ {
for y := 0; y < imageHeight; y++ {
dMin := dot(imageWidth, imageHeight)
var sMin int
for s := 0; s < nSites; s++ {
if d := dot(sx[s]-x, sy[s]-y); d < dMin {
sMin = s
dMin = d
}
}
img.SetNRGBA(x, y, sc[sMin])
}
}
// mark each site with a black box
black := image.NewUniform(color.Black)
for s := 0; s < nSites; s++ {
draw.Draw(img, image.Rect(sx[s]-2, sy[s]-2, sx[s]+2, sy[s]+2),
black, image.ZP, draw.Src)
}
return img
}
func dot(x, y int) int {
return x*x + y*y
}
func randomSites() (sx, sy []int) {
rand.Seed(time.Now().Unix())
sx = make([]int, nSites)
sy = make([]int, nSites)
for i := range sx {
sx[i] = rand.Intn(imageWidth)
sy[i] = rand.Intn(imageHeight)
}
return
}
func writePngFile(img image.Image) {
f, err := os.Create("voronoi.png")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
if err = png.Encode(f, img); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
if err = f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
Haskell
Uses the repa and repa-io libraries.
-- Compile with: ghc -O2 -fllvm -fforce-recomp -threaded --make
{-# LANGUAGE BangPatterns #-}
module Main where
import System.Random
import Data.Word
import Data.Array.Repa as Repa
import Data.Array.Repa.IO.BMP
{-# INLINE sqDistance #-}
sqDistance :: Word32 -> Word32 -> Word32 -> Word32 -> Word32
sqDistance !x1 !y1 !x2 !y2 = ((x1-x2)^2) + ((y1-y2)^2)
centers :: Int -> Int -> Array U DIM2 Word32
centers nCenters nCells =
fromListUnboxed (Z :. nCenters :. 2) $ take (2*nCenters) $
randomRs (0, fromIntegral nCells) (mkStdGen 1)
applyReduce2 arr f =
traverse arr (\(i :. j) -> i) $ \lookup (Z:.i) ->
f (lookup (Z:.i:.0)) (lookup (Z:.i:.1))
minimize1D arr = foldS f h t
where
indexed arr = traverse arr id (\src idx@(Z :. i) -> (src idx, (fromIntegral i)))
(Z :. n) = extent arr
iarr = indexed arr
h = iarr ! (Z :. 0)
t = extract (Z :. 1) (Z :. (n-1)) iarr
f min@(!valMin, !iMin ) x@(!val, !i) | val < valMin = x
| otherwise = min
voronoi :: Int -> Int -> Array D DIM2 Word32
voronoi nCenters nCells =
let
{-# INLINE cellReducer #-}
cellReducer = applyReduce2 (centers nCenters nCells)
{-# INLINE nearestCenterIndex #-}
nearestCenterIndex = snd . (Repa.! Z) . minimize1D
in
Repa.fromFunction (Z :. nCells :. nCells :: DIM2) $ \ (Z:.i:.j) ->
nearestCenterIndex $
cellReducer (sqDistance (fromIntegral i) (fromIntegral j))
genColorTable :: Int -> Array U DIM1 (Word8, Word8, Word8)
genColorTable n = fromListUnboxed (Z :. n) $ zip3 l1 l2 l3
where
randoms = randomRs (0,255) (mkStdGen 1)
(l1, rest1) = splitAt n randoms
(l2, rest2) = splitAt n rest1
l3 = take n rest2
colorize
:: Array U DIM1 (Word8, Word8, Word8)
-> Array D DIM2 Word32
-> Array D DIM2 (Word8, Word8, Word8)
colorize ctable = Repa.map $ \x -> ctable Repa.! (Z:. fromIntegral x)
main = do
let nsites = 150
let ctable = genColorTable nsites
voro <- computeP $ colorize ctable (voronoi nsites 512)
:: IO (Array U DIM2 (Word8, Word8, Word8))
writeImageToBMP "out.bmp" voro
Icon and Unicon
The sample images to the right show the screen size, number of sites, and metric used in the title bar.
![]()
![]()
link graphics,printf,strings
record site(x,y,colour) # site data position and colour
invocable all # needed for string metrics
procedure main(A) # voronoi
&window := open("Voronoi","g","bg=black") | stop("Unable to open window")
WAttrib("canvas=hidden") # figure out maximal size width & height
WAttrib(sprintf("size=%d,%d",WAttrib("displaywidth"),WAttrib("displayheight")))
WAttrib("canvas=maximal")
height := WAttrib("height")
width := WAttrib("width")
metrics := ["hypot","taxi","taxi3"] # different metrics
while case a := get(A) of { # command line arguments
"--sites" | "-s" : sites := 0 < integer(a := get(A)) | runerr(205,a)
"--height" | "-h" : height := 0 < (height >= integer(a := get(A))) | runerr(205,a)
"--width" | "-w" : width := 0 < (width >= integer(a := get(A))) | runerr(205,a)
"--metric" | "-m" : metric := ((a := get(A)) == !metrics) | runerr(205,a)
"--help" | "-?" : write("Usage:\n voronoi [[--sites|-s] n] ",
"[[--height|-h] pixels] [[--width|-w] pixels]",
"[[--metric|-m] metric_procedure]",
"[--help|-?]\n\n")
}
/metric := metrics[1] # default to normal
/sites := ?(r := integer(.1*width)) + r # sites = random .1 to .2 of width if not given
WAttrib(sprintf("label=Voronoi %dx%d %d %s",width,height,sites,metric))
WAttrib(sprintf("size=%d,%d",width,height))
x := "0123456789abcdef" # hex for random sites (colour)
siteL := []
every 1 to sites do # random sites
put(siteL, site(?width,?height,cat("#",?x,?x,?x,?x,?x,?x)))
VoronoiDiagram(width,height,siteL,metric) # Voronoi-ize it
WDone()
end
procedure hypot(x,y,site) # normal metric
return sqrt((x-site.x)^2 + (y-site.y)^2)
end
procedure taxi(x,y,site) # "taxi" metric
return abs(x-site.x)+abs(y-site.y)
end
procedure taxi3(x,y,site) # copied from a commented out version (TCL)
return (abs(x-site.x)^3+abs(y-site.y)^3)^(.3)
end
procedure VoronoiDiagram(width,height,siteL,metric)
/metric := hypot
every y := 1 to height & x := 1 to width do {
dist := width+height # anything larger than diagonal
every site := !siteL do {
if dist < (dt := metric(x,y,site)) then next # skip
else if dist >:= dt then Fg(site.colour) # site
else Fg("#000000") # unowned
DrawPoint(x,y)
}
}
Fg("Black")
every site := !siteL do # mark sites
DrawCircle(site.x,site.y,1)
end
printf.icn provides the printf family
graphics.icn provides graphics support
J
Explicit version
A straightforward solution: Generate random points and for each pixel find the index of the least distance. Note that the square root is avoided to improve performance.
NB. (number of points) voronoi (shape)
NB. Generates an array of indices of the nearest point
voronoi =: 4 :0
p =. (x,2) ?@$ y
(i.<./)@:(+/@:*:@:-"1&p)"1 ,"0/&i./ y
)
load'viewmat'
viewmat 25 voronoi 500 500
Another solution generates Voronoi cells from Delaunay triangulation. The page [[Voronoi diagram/J/Delaunay triangulation]] also contains a convex hull algorithm. This is a vector based approach instead of a pixel based approach and is about twice as fast for this task's example.
Tacit version
This a direct reformulation of the explicit version.
Voronoi=. ,"0/&i./@:] (i. <./)@:(+/@:*:@:-"1)"1 _ ] ?@$~ 2 ,~ [
viewmat 25 Voronoi 500 500 [ load'viewmat'
Delphi
procedure TForm1.Voronoi;
const
p = 3;
cells = 100;
size = 1000;
var
aCanvas : TCanvas;
px, py: array of integer;
color: array of Tcolor;
Img: TBitmap;
lastColor:Integer;
auxList: TList<TPoint>;
poligonlist : TDictionary<integer,TList<TPoint>>;
pointarray : array of TPoint;
n,i,x,y,k,j: Integer;
d1,d2: double;
function distance(x1,x2,y1,y2 :Integer) : Double;
begin
result := sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2)); ///Euclidian
// result := abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2); // Manhattan
// result := power(power(abs(x1 - x2), p) + power(abs(y1 - y2), p), (1 / p)); // Minkovski
end;
begin
poligonlist := TDictionary<integer,TList<Tpoint>>.create;
n := 0;
Randomize;
img := TBitmap.Create;
img.Width :=1000;
img.Height :=1000;
setlength(px,cells);
setlength(py,cells);
setlength(color,cells);
for i:= 0 to cells-1 do
begin
px[i] := Random(size);
py[i] := Random(size);
color[i] := Random(16777215);
auxList := TList<Tpoint>.Create;
poligonlist.Add(i,auxList);
end;
for x := 0 to size - 1 do
begin
lastColor:= 0;
for y := 0 to size - 1 do
begin
n:= 0;
for i := 0 to cells - 1 do
begin
d1:= distance(px[i], x, py[i], y);
d2:= distance(px[n], x, py[n], y);
if d1 < d2 then
begin
n := i;
end;
end;
if n <> lastColor then
begin
poligonlist[n].Add(Point(x,y));
poligonlist[lastColor].Add(Point(x,y));
lastColor := n;
end;
end;
poligonlist[n].Add(Point(x,y));
poligonlist[lastColor].Add(Point(x,y));
lastColor := n;
end;
for j := 0 to cells -1 do
begin
SetLength(pointarray, poligonlist[j].Count);
for I := 0 to poligonlist[j].Count - 1 do
begin
if Odd(i) then
pointarray[i] := poligonlist[j].Items[i];
end;
for I := 0 to poligonlist[j].Count - 1 do
begin
if not Odd(i) then
pointarray[i] := poligonlist[j].Items[i];
end;
Img.Canvas.Pen.Color := color[j];
Img.Canvas.Brush.Color := color[j];
Img.Canvas.Polygon(pointarray);
Img.Canvas.Pen.Color := clBlack;
Img.Canvas.Brush.Color := clBlack;
Img.Canvas.Rectangle(px[j] -2, py[j] -2, px[j] +2, py[j] +2);
end;
Canvas.Draw(0,0, img);
end;
Java
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Random;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Voronoi extends JFrame {
static double p = 3;
static BufferedImage I;
static int px[], py[], color[], cells = 100, size = 1000;
public Voronoi() {
super("Voronoi Diagram");
setBounds(0, 0, size, size);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
int n = 0;
Random rand = new Random();
I = new BufferedImage(size, size, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
px = new int[cells];
py = new int[cells];
color = new int[cells];
for (int i = 0; i < cells; i++) {
px[i] = rand.nextInt(size);
py[i] = rand.nextInt(size);
color[i] = rand.nextInt(16777215);
}
for (int x = 0; x < size; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < size; y++) {
n = 0;
for (byte i = 0; i < cells; i++) {
if (distance(px[i], x, py[i], y) < distance(px[n], x, py[n], y)) {
n = i;
}
}
I.setRGB(x, y, color[n]);
}
}
Graphics2D g = I.createGraphics();
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
for (int i = 0; i < cells; i++) {
g.fill(new Ellipse2D .Double(px[i] - 2.5, py[i] - 2.5, 5, 5));
}
try {
ImageIO.write(I, "png", new File("voronoi.png"));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
g.drawImage(I, 0, 0, this);
}
static double distance(int x1, int x2, int y1, int y2) {
double d;
d = Math.sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2)); // Euclidian
// d = Math.abs(x1 - x2) + Math.abs(y1 - y2); // Manhattan
// d = Math.pow(Math.pow(Math.abs(x1 - x2), p) + Math.pow(Math.abs(y1 - y2), p), (1 / p)); // Minkovski
return d;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Voronoi().setVisible(true);
}
}
JavaScript
Version 1
The obvious route to this in JavaScript would be to use Mike Bostock's D3.js library.
There are various examples of Voronoi tesselations, some dynamic:
https://bl.ocks.org/mbostock/d1d81455dc21e10f742f
some interactive:
https://bl.ocks.org/mbostock/4060366
and all with source code, at https://bl.ocks.org/mbostock
Version 2
I would agree: using D3.js library can be very helpful. But having stable and compact algorithm in Python (Sidef) made it possible to develop looking the same Voronoi diagram in "pure" JavaScript. A few custom helper functions simplified code, and they can be used for any other applications.



<!-- VoronoiD.html -->
<html>
<head><title>Voronoi diagram</title>
<script>
// HF#1 Like in PARI/GP: return random number 0..max-1
function randgp(max) {return Math.floor(Math.random()*max)}
// HF#2 Random hex color
function randhclr() {
return "#"+
("00"+randgp(256).toString(16)).slice(-2)+
("00"+randgp(256).toString(16)).slice(-2)+
("00"+randgp(256).toString(16)).slice(-2)
}
// HF#3 Metrics: Euclidean, Manhattan and Minkovski 3/20/17
function Metric(x,y,mt) {
if(mt==1) {return Math.sqrt(x*x + y*y)}
if(mt==2) {return Math.abs(x) + Math.abs(y)}
if(mt==3) {return(Math.pow(Math.pow(Math.abs(x),3) + Math.pow(Math.abs(y),3),0.33333))}
}
// Plotting Voronoi diagram. aev 3/10/17
function pVoronoiD() {
var cvs=document.getElementById("cvsId");
var ctx=cvs.getContext("2d");
var w=cvs.width, h=cvs.height;
var x=y=d=dm=j=0, w1=w-2, h1=h-2;
var n=document.getElementById("sites").value;
var mt=document.getElementById("mt").value;
var X=new Array(n), Y=new Array(n), C=new Array(n);
ctx.fillStyle="white"; ctx.fillRect(0,0,w,h);
for(var i=0; i<n; i++) {
X[i]=randgp(w1); Y[i]=randgp(h1); C[i]=randhclr();
}
for(y=0; y<h1; y++) {
for(x=0; x<w1; x++) {
dm=Metric(h1,w1,mt); j=-1;
for(var i=0; i<n; i++) {
d=Metric(X[i]-x,Y[i]-y,mt)
if(d<dm) {dm=d; j=i;}
}//fend i
ctx.fillStyle=C[j]; ctx.fillRect(x,y,1,1);
}//fend x
}//fend y
ctx.fillStyle="black";
for(var i=0; i<n; i++) {
ctx.fillRect(X[i],Y[i],3,3);
}
}
</script></head>
<body style="font-family: arial, helvatica, sans-serif;">
<b>Please input number of sites: </b>
<input id="sites" value=100 type="number" min="10" max="150" size="3">
<b>Metric: </b>
<select id="mt">
<option value=1 selected>Euclidean</option>
<option value=2>Manhattan</option>
<option value=3>Minkovski</option>
</select>
<input type="button" value="Plot it!" onclick="pVoronoiD();">
<h3>Voronoi diagram</h3>
<canvas id="cvsId" width="640" height="640" style="border: 2px inset;"></canvas>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Page demonstrating Voronoi diagram for any reasonable number of sites and selected metric.
Right clicking on canvas with image allows you to save it as png-file, for example.
Julia
First version generates an image with random colors as centroids for the voronoi tesselation:
using Images
function voronoi(w, h, n_centroids)
dist = (point,vector) -> sqrt.((point[1].-vector[:,1]).^2 .+ (point[2].-vector[:,2]).^2)
dots = [rand(1:h, n_centroids) rand(1:w, n_centroids) rand(RGB{N0f8}, n_centroids)]
img = zeros(RGB{N0f8}, h, w)
for x in 1:h, y in 1:w
distances = dist([x,y],dots) # distance
nn = findmin(distances)[2]
img[x,y] = dots[nn,:][3]
end
return img
end
img = voronoi(800, 600, 200)
Second version takes an image as an input, samples random centroids for the voronoi cells, and assigns every pixel within that cell the color of the centroid:
using TestImages, Images
function voronoi_img!(img, n_centroids)
n,m = size(img)
w = minimum([n,m])
dist = (point,vector) -> sqrt.((point[1].-vector[:,1]).^2 .+ (point[2].-vector[:,2]).^2)
dots = [rand(1:n, n_centroids) rand(1:m, n_centroids)]
c = []
for i in 1:size(dots,1)
p = dots[i,:]
append!(c, [img[p[1],p[2]]])
end
dots = [dots c]
for x in 1:n, y in 1:m
distances = dist([x,y],dots) # distance
nn = findmin(distances)[2]
img[x,y] = dots[nn,:][3]
end
end
img = testimage("mandrill")
voronoi_img!(img, 300)
Kotlin
Translated from Java.
// version 1.1.3
import java.awt.Color
import java.awt.Graphics
import java.awt.Graphics2D
import java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage
import java.util.Random
import javax.swing.JFrame
fun distSq(x1: Int, x2: Int, y1: Int, y2: Int): Int {
val x = x1 - x2
val y = y1 - y2
return x * x + y * y
}
class Voronoi(val cells: Int, val size: Int) : JFrame("Voronoi Diagram") {
val bi: BufferedImage
init {
setBounds(0, 0, size, size)
defaultCloseOperation = EXIT_ON_CLOSE
val r = Random()
bi = BufferedImage(size, size, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB)
val px = IntArray(cells) { r.nextInt(size) }
val py = IntArray(cells) { r.nextInt(size) }
val cl = IntArray(cells) { r.nextInt(16777215) }
for (x in 0 until size) {
for (y in 0 until size) {
var n = 0
for (i in 0 until cells) {
if (distSq(px[i], x, py[i], y) < distSq(px[n], x, py[n], y)) n = i
}
bi.setRGB(x, y, cl[n])
}
}
val g = bi.createGraphics()
g.color = Color.BLACK
for (i in 0 until cells) {
g.fill(Ellipse2D.Double(px[i] - 2.5, py[i] - 2.5, 5.0, 5.0))
}
}
override fun paint(g: Graphics) {
g.drawImage(bi, 0, 0, this)
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
Voronoi(70, 700).isVisible = true
}
Liberty BASIC
For first site it fills the table with distances to that site. For other sites it looks at vertical lines left and right from its location. If no place on a vertical line is closer to the current site, then there's no point looking further left or right. Don't bother square-rooting to get distances..
WindowWidth =600
WindowHeight =600
sites = 100
xEdge = 400
yEdge = 400
graphicbox #w.gb1, 10, 10, xEdge, yEdge
open "Voronoi neighbourhoods" for window as #w
#w "trapclose quit"
#w.gb1 "down ; fill black ; size 4"
#w.gb1 "font courier_new 12"
dim townX( sites), townY( sites), col$( sites)
for i =1 to sites
townX( i) =int( xEdge *rnd( 1))
townY( i) =int( yEdge *rnd( 1))
col$( i) = int( 256 *rnd( 1)); " "; int( 256 *rnd( 1)); " "; int( 256 *rnd( 1))
#w.gb1 "color "; col$( i)
#w.gb1 "set "; townX( i); " "; townY( i)
next i
#w.gb1 "size 1"
dim nearestIndex(xEdge, yEdge)
dim dist(xEdge, yEdge)
start = time$("ms")
'fill distance table with distances from the first site
for x = 0 to xEdge - 1
for y = 0 to yEdge - 1
dist(x, y) = (townX(1) - x) ^ 2 + (townY(1) - y) ^ 2
nearestIndex(x, y) = 1
next y
next x
#w.gb1 "color darkblue"
'for other towns
for i = 2 to sites
'display some progress
#w.gb1 "place 0 20"
#w.gb1 "\computing: "; using("###.#", i / sites * 100); "%"
'look left
for x = townX(i) to 0 step -1
if not(checkRow(i, x,0, yEdge - 1)) then exit for
next x
'look right
for x = townX(i) + 1 to xEdge - 1
if not(checkRow(i, x, 0, yEdge - 1)) then exit for
next x
scan
next i
for x = 0 to xEdge - 1
for y =0 to yEdge - 1
#w.gb1 "color "; col$(nearestIndex(x, y))
startY = y
nearest = nearestIndex(x, y)
for y = y + 1 to yEdge
if nearestIndex(x, y) <> nearest then y = y - 1 : exit for
next y
#w.gb1 "line "; x; " "; startY; " "; x; " "; y + 1
next y
next x
#w.gb1 "color black; size 4"
for i =1 to sites
#w.gb1 "set "; townX( i); " "; townY( i)
next i
print time$("ms") - start
wait
sub quit w$
close #w$
end
end sub
function checkRow(site, x, startY, endY)
dxSquared = (townX(site) - x) ^ 2
for y = startY to endY
dSquared = (townY(site) - y) ^ 2 + dxSquared
if dSquared <= dist(x, y) then
dist(x, y) = dSquared
nearestIndex(x, y) = site
checkRow = 1
end if
next y
end function
Lua
Works with LÖVE 0.10.1. Translated from Python.
function love.load( )
love.math.setRandomSeed( os.time( ) ) --set the random seed
keys = { } --an empty table where we will store key presses
number_cells = 50 --the number of cells we want in our diagram
--draw the voronoi diagram to a canvas
voronoiDiagram = generateVoronoi( love.graphics.getWidth( ), love.graphics.getHeight( ), number_cells )
end
function hypot( x, y )
return math.sqrt( x*x + y*y )
end
function generateVoronoi( width, height, num_cells )
canvas = love.graphics.newCanvas( width, height )
local imgx = canvas:getWidth( )
local imgy = canvas:getHeight( )
local nx = { }
local ny = { }
local nr = { }
local ng = { }
local nb = { }
for a = 1, num_cells do
table.insert( nx, love.math.random( 0, imgx ) )
table.insert( ny, love.math.random( 0, imgy ) )
table.insert( nr, love.math.random( 0, 255 ) )
table.insert( ng, love.math.random( 0, 255 ) )
table.insert( nb, love.math.random( 0, 255 ) )
end
love.graphics.setColor( { 255, 255, 255 } )
love.graphics.setCanvas( canvas )
for y = 1, imgy do
for x = 1, imgx do
dmin = hypot( imgx-1, imgy-1 )
j = -1
for i = 1, num_cells do
d = hypot( nx[i]-x, ny[i]-y )
if d < dmin then
dmin = d
j = i
end
end
love.graphics.setColor( { nr[j], ng[j], nb[j] } )
love.graphics.points( x, y )
end
end
--reset color
love.graphics.setColor( { 255, 255, 255 } )
--draw points
for b = 1, num_cells do
love.graphics.points( nx[b], ny[b] )
end
love.graphics.setCanvas( )
return canvas
end
--RENDER
function love.draw( )
--reset color
love.graphics.setColor( { 255, 255, 255 } )
--draw diagram
love.graphics.draw( voronoiDiagram )
--draw drop shadow text
love.graphics.setColor( { 0, 0, 0 } )
love.graphics.print( "space: regenerate\nesc: quit", 1, 1 )
--draw text
love.graphics.setColor( { 200, 200, 0 } )
love.graphics.print( "space: regenerate\nesc: quit" )
end
--CONTROL
function love.keyreleased( key )
if key == 'space' then
voronoiDiagram = generateVoronoi( love.graphics.getWidth( ), love.graphics.getHeight( ), number_cells )
elseif key == 'escape' then
love.event.quit( )
end
end
Mathematica
Needs["ComputationalGeometry`"]
DiagramPlot[{{4.4, 14}, {6.7, 15.25}, {6.9, 12.8}, {2.1, 11.1}, {9.5, 14.9}, {13.2, 11.9}, {10.3, 12.3},
{6.8, 9.5}, {3.3, 7.7}, {0.6, 5.1}, {5.3, 2.4}, {8.45, 4.7}, {11.5, 9.6}, {13.8, 7.3}, {12.9, 3.1}, {11, 1.1}}]
MK-61/52
0 П4
0 П5
ИП0 1 - x^2 ИП1 1 - x^2 + КвКор П3
9 П6
КИП6 П8 {x} 2 10^x * П9
[x] ИП5 - x^2 ИП9 {x} 2 10^x * ИП4 - x^2 + КвКор П9
ИП3 - x<0 47 ИП9 П3 ИП6 П7
ИП6 ИП2 - 9 - x>=0 17
КИП7 [x] С/П
КИП5 ИП5 ИП1 - x>=0 04
КИП4 ИП4 ИП0 - x>=0 02
''Input'': Р0 - diagram width; Р1 - diagram height; Р0 - number of the points; РA - РE - coordinates and colors of the points in format ''C,XXYY'' (example: 3,0102).
Example of the manually compiled output (graphical output from this class of devices is missing):
{| border="0" width="250" |- align="center" bgcolor="#F0C0C0" |·||·||·||·||·||·||·||·||·||· |- align="center" bgcolor="#F0C0C0" |·||·||·||·||·||·||·||·||·||· |- align="center" bgcolor="#F0C0C0" |·||·||·||·||·||·||·||·||·||· |- align="center" bgcolor="#F0C0C0" |·||·||·||•||·||·||·||·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |· |- align="center" bgcolor="#F0C0C0" | bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·||·||·||·||·|||·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |· |- align="center" bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·||·||·||·|| bgcolor="#F0C0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#F0C0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |· |- align="center" bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·||·||•||·||·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |· |- align="center" bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·||·||·||·||·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0C0F0" |· |- align="center" bgcolor="#C0C0F0" | bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·||·||·||•||·||· |- align="center" bgcolor="#C0C0F0" | bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·|| bgcolor="#C0F0C0" |·||·||·||·||·||·||· |}
Nim
Works with nim 0.19.4.
from sequtils import newSeqWith
from random import rand, randomize
from times import now
import libgd
const
img_width = 400
img_height = 300
nSites = 20
proc dot(x, y: int): int = x * x + y * y
proc generateVoronoi(img: gdImagePtr) =
randomize(cast[int64](now()))
# random sites
let sx = newSeqWith(nSites, rand(img_width))
let sy = newSeqWith(nSites, rand(img_height))
# generate a random color for each site
let sc = newSeqWith(nSites, img.setColor(rand(255), rand(255), rand(255)))
# generate diagram by coloring each pixel with color of nearest site
for x in 0 ..< img_width:
for y in 0 ..< img_height:
var dMin = dot(img_width, img_height)
var sMin: int
for s in 0 ..< nSites:
if (let d = dot(sx[s] - x, sy[s] - y); d) < dMin:
(sMin, dMin) = (s, d)
img.setPixel(point=[x, y], color=sc[sMin])
# mark each site with a black box
let black = img.setColor(0x000000)
for s in 0 ..< nSites:
img.drawRectangle(
startCorner=[sx[s] - 2, sy[s] - 2],
endCorner=[sx[s] + 2, sy[s] + 2],
color=black,
fill=true)
proc main() =
withGd imageCreate(img_width, img_height, trueColor=true) as img:
img.generateVoronoi()
let png_out = open("outputs/voronoi_diagram.png", fmWrite)
img.writePng(png_out)
png_out.close()
main()
OCaml
Works with OCaml 4.07.1.
let n_sites = 220
let size_x = 640
let size_y = 480
let sq2 ~x ~y =
(x * x + y * y)
let rand_int_range a b =
a + Random.int (b - a + 1)
let nearest_site ~site ~x ~y =
let ret = ref 0 in
let dist = ref 0 in
Array.iteri (fun k (sx, sy) ->
let d = sq2 (x - sx) (y - sy) in
if k = 0 || d < !dist then begin
dist := d;
ret := k;
end
) site;
!ret
let gen_map ~site ~rgb =
let nearest = Array.make (size_x * size_y) 0 in
let buf = Bytes.create (3 * size_x * size_y) in
for y = 0 to pred size_y do
for x = 0 to pred size_x do
nearest.(y * size_x + x) <-
nearest_site ~site ~x ~y;
done;
done;
for i = 0 to pred (size_y * size_x) do
let j = i * 3 in
let r, g, b = rgb.(nearest.(i)) in
Bytes.set buf (j+0) (char_of_int r);
Bytes.set buf (j+1) (char_of_int g);
Bytes.set buf (j+2) (char_of_int b);
done;
Printf.printf "P6\n%d %d\n255\n" size_x size_y;
print_bytes buf;
;;
let () =
Random.self_init ();
let site =
Array.init n_sites (fun i ->
(Random.int size_x,
Random.int size_y))
in
let rgb =
Array.init n_sites (fun i ->
(rand_int_range 160 255,
rand_int_range 40 160,
rand_int_range 20 140))
in
gen_map ~site ~rgb
Perl
Translated from Perl 6.
use strict;
use warnings;
use Imager;
my %type = (
Taxicab => sub { my($px, $py, $x, $y) = @_; abs($px - $x) + abs($py - $y) },
Euclidean => sub { my($px, $py, $x, $y) = @_; ($px - $x)**2 + ($py - $y)**2 },
Minkowski => sub { my($px, $py, $x, $y) = @_; abs($px - $x)**3 + abs($py - $y)**3 },
);
my($xmax, $ymax) = (400, 400);
my @domains;
for (1..30) {
push @domains, {
x => int 5 + rand $xmax-10,
y => int 5 + rand $ymax-10,
rgb => [int rand 255, int rand 255, int rand 255]
}
}
for my $type (keys %type) {
our $img = Imager->new(xsize => $xmax, ysize => $ymax, channels => 3);
voronoi($type, $xmax, $ymax, @domains);
dot(1,@domains);
$img->write(file => "voronoi-$type.png");
sub voronoi {
my($type, $xmax, $ymax, @d) = @_;
for my $x (0..$xmax) {
for my $y (0..$ymax) {
my $i = 0;
my $d = 10e6;
for (0..$#d) {
my $dd = &{$type{$type}}($d[$_]{'x'}, $d[$_]{'y'}, $x, $y);
if ($dd < $d) { $d = $dd; $i = $_ }
}
$img->setpixel(x => $x, y => $y, color => $d[$i]{rgb} );
}
}
}
sub dot {
my($radius, @d) = @_;
for (0..$#d) {
my $dx = $d[$_]{'x'};
my $dy = $d[$_]{'y'};
for my $x ($dx-$radius .. $dx+$radius) {
for my $y ($dy-$radius .. $dy+$radius) {
$img->setpixel(x => $x, y => $y, color => [0,0,0]);
}
}
}
}
}
Perl 6
Works with Rakudo 2018.09 Translated from Python. Perhaps "Inspired by Python" would be more accurate.
Generates a Euclidean, a Taxicab and a Minkowski Voronoi diagram using the same set of domain points and colors.
use Image::PNG::Portable;
my @bars = '▁▂▃▅▆▇▇▆▅▃▂▁'.comb;
my %type = ( # Voronoi diagram type distance calculation
'Taxicab' => sub ($px, $py, $x, $y) { ($px - $x).abs + ($py - $y).abs },
'Euclidean' => sub ($px, $py, $x, $y) { ($px - $x)² + ($py - $y)² },
'Minkowski' => sub ($px, $py, $x, $y) { ($px - $x)³.abs + ($py - $y)³.abs },
);
my $width = 400;
my $height = 400;
my $dots = 30;
my @domains = map { Hash.new(
'x' => (5..$width-5).roll,
'y' => (5..$height-5).roll,
'rgb' => [(64..255).roll xx 3]
) }, ^$dots;
for %type.keys -> $type {
print "\nGenerating $type diagram... ", ' ' x @bars;
my $img = voronoi(@domains, :w($width), :h($height), :$type);
@domains.map: *.&dot($img);
$img.write: "Voronoi-{$type}-perl6.png";
}
sub voronoi (@domains, :$w, :$h, :$type) {
my $png = Image::PNG::Portable.new: :width($w), :height($h);
(^$w).race.map: -> $x {
print "\b" x 2+@bars, @bars.=rotate(1).join , ' ';
for ^$h -> $y {
my ($, $i) = min @domains.map: { %type{$type}(%($_)<x>, %($_)<y>, $x, $y), $++ };
$png.set: $x, $y, |@domains[$i]<rgb>
}
}
$png
}
sub dot (%h, $png, $radius = 3) {
for (%h<x> X+ -$radius .. $radius) X (%h<y> X+ -$radius .. $radius) -> ($x, $y) {
$png.set($x, $y, 0, 0, 0) if ( %h<x> - $x + (%h<y> - $y) * i ).abs <= $radius;
}
}
See Euclidean, Taxicab, and Minkowski Voronoi diagram example images.
Phix
Translated from Liberty_BASIC. Lifted the calculation strategy from Liberty Basic. Can resize, double or halve sites (press +/-), and toggle between Euclid, Manhattan, and Minkowski (press e/m/w).
--
-- demo\rosetta\VoronoiDiagram.exw
--
include pGUI.e
Ihandle dlg, canvas, timer
cdCanvas cddbuffer, cdcanvas
-- Stop any current drawing process before starting a new one:
-- Without this it /is/ going to crash, if it tries to finish
-- drawing all 100 sites, when there are now only 50, for eg.
integer timer_active = 0
integer nsites = 200
integer last_width = -1, last_height
sequence siteX, siteY, siteC
enum EUCLID, MANHATTAN, MINKOWSKI
constant dmodes = {"Euclid", "Manhattan", "Minkowski"}
integer dmode = EUCLID,
drawn = 0 -- (last dmode actually shown)
function distance(integer x1,y1, x2,y2)
atom d
x1 -= x2
y1 -= y2
switch dmode do
case EUCLID: d = x1*x1+y1*y1 -- (no need for sqrt)
case MANHATTAN: d = abs(x1)+abs(y1)
case MINKOWSKI: d = power(abs(x1),3)+power(abs(y1),3) -- ("" power(d,1/3))
end switch
return d
end function
sequence nearestIndex, dist
function checkRow(integer site, integer x, integer height)
bool res = false
atom dxSquared
integer x1 = siteX[site]-x
switch dmode do
case EUCLID: dxSquared = x1*x1
case MANHATTAN: dxSquared = abs(x1)
case MINKOWSKI: dxSquared = power(abs(x1),3)
end switch
for y=1 to height do
-- atom dSquared = distance(siteX[site],siteY[site],x,y) -- (sub-optimal..)
atom dSquared
integer y1 = siteY[site]-y
switch dmode do
case EUCLID: dSquared = dxSquared + y1*y1
case MANHATTAN: dSquared = dxSquared + abs(y1)
case MINKOWSKI: dSquared = dxSquared + power(abs(y1),3)
end switch
if dSquared<=dist[x,y] then
dist[x,y] = dSquared
nearestIndex[x,y] = site
res = true
end if
end for
return res
end function
function redraw_cb(Ihandle /*ih*/, integer /*posx*/, integer /*posy*/)
integer {width, height} = IupGetIntInt(canvas, "DRAWSIZE")
if width!=last_width
or height!=last_height
or nsites!=length(siteX) then
if nsites<1 then nsites = 1 end if
siteX = sq_rand(repeat(width,nsites))
siteY = sq_rand(repeat(height,nsites))
siteC = sq_rand(repeat(#FFFFFF,nsites))
last_width = width
last_height = height
drawn = 0
end if
if drawn!=dmode -- (prevent double-draw, and)
and not timer_active then -- (drawing when rug moved..)
drawn = dmode
cdCanvasActivate(cddbuffer)
atom t0 = time(), t1
t1 = time()+0.25
nearestIndex = repeat(repeat(1,height),width)
dist = repeat(repeat(0,height),width)
-- fill distance table with distances from the first site
integer x1 = siteX[1], y1 = siteY[1]
for x=1 to width do
for y=1 to height do
dist[x,y] = distance(x1,y1,x,y)
end for
if timer_active then exit end if
end for
--for other towns
for i=2 to nsites do
-- look left
for x=siteX[i] to 1 by -1 do
if not checkRow(i, x, height) then exit end if
end for
-- look right
for x=siteX[i]+1 to width do
if not checkRow(i, x, height) then exit end if
end for
if timer_active then exit end if
if time()>t1 then
IupSetStrAttribute(dlg, "TITLE", "Voronoi diagram (generating - %3.2f%%)",{100*i/nsites})
IupFlush()
t1 = time()+0.25
end if
end for
t1 = time()
for y=1 to height do
integer nearest = nearestIndex[1,y]
integer s = 1
for x=2 to width do
if nearestIndex[x,y]<>nearest then
cdCanvasSetForeground(cddbuffer, siteC[nearest])
cdCanvasLine(cddbuffer, s-1, y-1, x-2, y-1)
nearest = nearestIndex[x,y]
s = x
end if
end for
if timer_active then exit end if
cdCanvasSetForeground(cddbuffer, siteC[nearest])
cdCanvasLine(cddbuffer, s-1, y-1, width-1, y-1)
end for
if not timer_active then
cdCanvasSetForeground(cddbuffer, CD_BLACK)
for i=1 to nsites do
cdCanvasSector(cddbuffer, siteX[i], siteY[i], 2, 2, 0, 360)
end for
cdCanvasFlush(cddbuffer)
IupSetStrAttribute(dlg, "TITLE", "Voronoi diagram - %s, %dx%d, %d sites, %3.2fs",{dmodes[dmode],width,height,nsites,time()-t0})
end if
end if
return IUP_DEFAULT
end function
function map_cb(Ihandle ih)
cdcanvas = cdCreateCanvas(CD_IUP, ih)
cddbuffer = cdCreateCanvas(CD_DBUFFER, cdcanvas)
cdCanvasSetBackground(cddbuffer, CD_WHITE)
cdCanvasSetForeground(cddbuffer, CD_BLACK)
return IUP_DEFAULT
end function
function esc_close(Ihandle /*ih*/, atom c)
if c=K_ESC then return IUP_CLOSE end if
integer wasdmode = dmode
switch c do
case '+': nsites *= 2
case '-': nsites = max(floor(nsites/2),1)
case 'E','e': dmode = EUCLID
case 'M','m': dmode = MANHATTAN
case 'W','w': dmode = MINKOWSKI
end switch
if dmode!=wasdmode
or nsites!=length(siteX) then
-- give any current drawing process 0.1s to abandon:
timer_active = 1
IupStoreAttribute(timer, "RUN", "YES")
-- IupUpdate(canvas)
end if
return IUP_CONTINUE
end function
function timer_cb(Ihandle /*ih*/)
timer_active = 0
IupStoreAttribute(timer, "RUN", "NO")
IupUpdate(canvas)
return IUP_IGNORE
end function
procedure main()
IupOpen()
canvas = IupCanvas(NULL)
IupSetAttribute(canvas, "RASTERSIZE", "600x400") -- initial size
IupSetCallback(canvas, "MAP_CB", Icallback("map_cb"))
timer = IupTimer(Icallback("timer_cb"), 100, 0) -- (inactive)
dlg = IupDialog(canvas)
IupSetAttribute(dlg, "TITLE", "Voronoi diagram")
IupSetCallback(dlg, "K_ANY", Icallback("esc_close"))
IupSetCallback(canvas, "ACTION", Icallback("redraw_cb"))
IupMap(dlg)
IupSetAttribute(canvas, "RASTERSIZE", NULL) -- release the minimum limitation
IupShowXY(dlg,IUP_CENTER,IUP_CENTER)
IupMainLoop()
IupClose()
end procedure
main()
Prolog
Works with SWI-Prolog and XPCE.
3 Voronoi diagrams are given for the same sites, one with the Manhattan distance, one with the Euclidean distance and the last with the Minkowski distance (order 3).
:- dynamic pt/6.
voronoi :-
V is random(20) + 20,
retractall(pt(_,_,_,_)),
forall(between(1, V, I),
( X is random(390) + 5,
Y is random(390) + 5,
R is random(65535),
G is random(65535),
B is random(65535),
assertz(pt(I,X,Y, R, G, B))
)),
voronoi(manhattan, V),
voronoi(euclide, V),
voronoi(minkowski_3, V).
voronoi(Distance, V) :-
sformat(A, 'Voronoi 400X400 ~w ~w', [V, Distance]),
new(D, window(A)),
send(D, size, size(400,400)),
new(Img, image(@nil, width := 400, height := 400 , kind := pixmap)),
% get the list of the sites
bagof((N, X, Y), R^G^B^pt(N, X, Y, R, G, B), L),
forall(between(0,399, I),
forall(between(0,399, J),
( get_nearest_site(V, Distance, I, J, L, S),
pt(S, _, _, R, G, B),
send(Img, pixel(I, J, colour(@default, R, G, B)))))),
new(Bmp, bitmap(Img)),
send(D, display, Bmp, point(0,0)),
send(D, open).
% define predicatea foldl (functionnal spirit)
foldl([], _Pred, R, R).
foldl([H | T], Pred, Acc, R) :-
call(Pred, H, Acc, R1),
foldl(T, Pred, R1, R).
% predicate for foldl
compare(Distance, XP, YP, (N, X, Y), (D, S), R) :-
call(Distance, XP, YP, X, Y, DT),
( DT < D -> R = (DT, N) ; R = (D, S)).
% use of a fake site for the init of foldl
get_nearest_site(Distance, I, J, L, S) :-
foldl(L, compare(Distance, I, J), (65535, nil), (_, S)).
manhattan(X1, Y1, X2, Y2, D) :-
D is abs(X2 - X1) + abs(Y2-Y1).
euclide(X1, Y1, X2, Y2, D) :-
D is sqrt((X2 - X1)**2 + (Y2-Y1)**2).
minkowski_3(X1, Y1, X2, Y2, D) :-
D is (abs(X2 - X1)**3 + abs(Y2-Y1)**3)**0.33.



PureBasic
Euclidean

Structure VCoo
x.i: y.i
Colour.i: FillColour.i
EndStructure
Macro RandInt(MAXLIMIT)
Int(MAXLIMIT*(Random(#MAXLONG)/#MAXLONG))
EndMacro
Macro SQ2(X, Y)
((X)*(X) + (Y)*(Y))
EndMacro
Procedure GenRandomPoints(Array a.VCoo(1), xMax, yMax, cnt)
Protected i, j, k, l
cnt-1
Dim a(cnt)
For i=0 To cnt
a(i)\x = RandInt(xMax): a(i)\y = RandInt(yMax)
j = RandInt(255): k = RandInt(255): l = RandInt(255)
a(i)\Colour = RGBA(j, k, l, 255)
a(i)\FillColour = RGBA(255-j, 255-k, 255-l, 255)
Next i
ProcedureReturn #True
EndProcedure
Procedure MakeVoronoiDiagram(Array a.VCoo(1),xMax, yMax) ; Euclidean
Protected i, x, y, img, dist.d, dt.d
img = CreateImage(#PB_Any, xMax+1, yMax+1)
If StartDrawing(ImageOutput(img))
For y=0 To yMax
For x=0 To xMax
dist = Infinity()
For i=0 To ArraySize(a())
dt = SQ2(x-a(i)\x, y-a(i)\y)
If dt > dist
Continue
ElseIf dt < dist
dist = dt
Plot(x,y,a(i)\FillColour)
Else ; 'Owner ship' is unclear, set pixel to transparent.
Plot(x,y,RGBA(0, 0, 0, 0))
EndIf
Next
Next
Next
For i=0 To ArraySize(a())
Circle(a(i)\x, a(i)\y, 1, a(i)\Colour)
Next
StopDrawing()
EndIf
ProcedureReturn img
EndProcedure
; Main code
Define img, x, y, file$
Dim V.VCoo(0)
x = 640: y = 480
If Not GenRandomPoints(V(), x, y, 150): End: EndIf
img = MakeVoronoiDiagram(V(), x, y)
If img And OpenWindow(0, 0, 0, x, y, "Voronoi Diagram in PureBasic", #PB_Window_SystemMenu)
ImageGadget(0, 0, 0, x, y, ImageID(img))
Repeat: Until WaitWindowEvent() = #PB_Event_CloseWindow
EndIf
UsePNGImageEncoder()
file$ = SaveFileRequester("Save Image?", "Voronoi_Diagram_in_PureBasic.png", "PNG|*.png", 0)
If file$ <> ""
SaveImage(img, file$, #PB_ImagePlugin_PNG)
EndIf
Taxicab
Structure VCoo
x.i: y.i
Colour.i: FillColour.i
EndStructure
Macro RandInt(MAXLIMIT)
Int(MAXLIMIT*(Random(#MAXLONG)/#MAXLONG))
EndMacro
Procedure GenRandomPoints(Array a.VCoo(1), xMax, yMax, cnt)
Protected i, j, k, l
cnt-1
Dim a(cnt)
For i=0 To cnt
a(i)\x = RandInt(xMax): a(i)\y = RandInt(yMax)
j = RandInt(255): k = RandInt(255): l = RandInt(255)
a(i)\Colour = RGBA(j, k, l, 255)
a(i)\FillColour = RGBA(255-j, 255-k, 255-l, 255)
Next i
ProcedureReturn #True
EndProcedure
Procedure MakeVoronoiDiagram(Array a.VCoo(1),xMax, yMax)
Protected i, x, y, img, dist, dt, dx, dy
img = CreateImage(#PB_Any, xMax+1, yMax+1, 32)
If StartDrawing(ImageOutput(img))
For y=0 To yMax
For x=0 To xMax
dist = #MAXLONG
For i=0 To ArraySize(a())
dx = x-a(i)\x
dy = y-a(i)\y
dt = Sign(dx)*dx + Sign(dy)*dy
If dt > dist ; no update
Continue
ElseIf dt < dist ; an new 'owner' is found
dist = dt
Plot(x,y,a(i)\FillColour)
Else ; dt = dist
Plot(x,y,RGBA(0,0,0,0)) ; no clear 'owner', make the pixel transparent
EndIf
Next
Next
Next
For i=0 To ArraySize(a())
Circle(a(i)\x, a(i)\y, 1, a(i)\Colour)
Next
StopDrawing()
EndIf
ProcedureReturn img
EndProcedure
; Main code
Define img, x, y, file$
Dim V.VCoo(0)
x = 640: y = 480
If Not GenRandomPoints(V(), x, y, 150): End: EndIf
img = MakeVoronoiDiagram(V(), x, y)
If img And OpenWindow(0, 0, 0, x, y, "Voronoi Diagram in PureBasic", #PB_Window_SystemMenu)
ImageGadget(0, 0, 0, x, y, ImageID(img))
Repeat: Until WaitWindowEvent() = #PB_Event_CloseWindow
EndIf
UsePNGImageEncoder()
file$ = SaveFileRequester("Save Image?", "Voronoi_Diagram_in_PureBasic.png", "PNG|*.png", 0)
If file$ <> ""
SaveImage(img, file$, #PB_ImagePlugin_PNG)
EndIf
Python
This implementation takes in a list of points, each point being a tuple and returns a dictionary consisting of all the points at a given site.
from PIL import Image
import random
import math
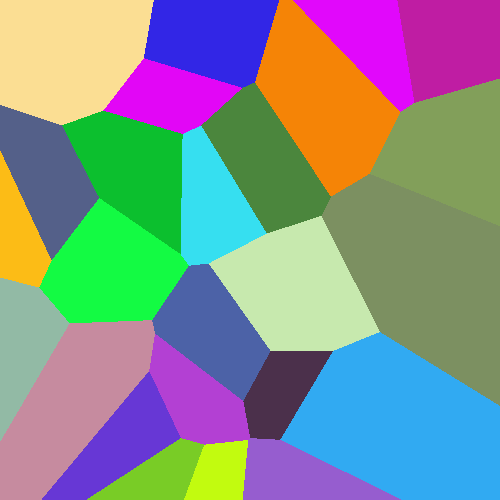
def generate_voronoi_diagram(width, height, num_cells):
image = Image.new("RGB", (width, height))
putpixel = image.putpixel
imgx, imgy = image.size
nx = []
ny = []
nr = []
ng = []
nb = []
for i in range(num_cells):
nx.append(random.randrange(imgx))
ny.append(random.randrange(imgy))
nr.append(random.randrange(256))
ng.append(random.randrange(256))
nb.append(random.randrange(256))
for y in range(imgy):
for x in range(imgx):
dmin = math.hypot(imgx-1, imgy-1)
j = -1
for i in range(num_cells):
d = math.hypot(nx[i]-x, ny[i]-y)
if d < dmin:
dmin = d
j = i
putpixel((x, y), (nr[j], ng[j], nb[j]))
image.save("VoronoiDiagram.png", "PNG")
image.show()
generate_voronoi_diagram(500, 500, 25)
Output:

R
One of the R's great powers is its unlimited number of packages, virtually thousands of them. For any applications big or small you can find a package. In case of Voronoi diagram there are many of packages, e.g.: deldir, alphahull, dismo, ggplot, ggplot2, tripack, CGAL, etc. Not to mention all linked packages. Do you need random colors? Again, find a few packages more...
So, I've decided to use proven algorithms instead. Result - small compact code and beautiful diagrams with any reasonable amount of sites. A few custom helper functions simplified code, and they can be used for any other applications.
If you have not a super fast computer, you can watch animation of plotting in "R Graphics" sub-window of the "RGui" window. Translated from JavaScript v.#2. Works with R|3.3.3 and above



## HF#1 Random Hex color
randHclr <- function() {
m=255;r=g=b=0;
r <- sample(0:m, 1, replace=TRUE);
g <- sample(0:m, 1, replace=TRUE);
b <- sample(0:m, 1, replace=TRUE);
return(rgb(r,g,b,maxColorValue=m));
}
## HF#2 Metrics: Euclidean, Manhattan and Minkovski
Metric <- function(x, y, mt) {
if(mt==1) {return(sqrt(x*x + y*y))}
if(mt==2) {return(abs(x) + abs(y))}
if(mt==3) {return((abs(x)^3 + abs(y)^3)^0.33333)}
}
## Plotting Voronoi diagram. aev 3/12/17
## ns - number of sites, fn - file name, ttl - plot title.
## mt - type of metric: 1 - Euclidean, 2 - Manhattan, 3 - Minkovski.
pVoronoiD <- function(ns, fn="", ttl="",mt=1) {
cat(" *** START VD:", date(), "\n");
if(mt<1||mt>3) {mt=1}; mts=""; if(mt>1) {mts=paste0(", mt - ",mt)};
m=640; i=j=k=m1=m-2; x=y=d=dm=0;
if(fn=="") {pf=paste0("VDR", mt, ns, ".png")} else {pf=paste0(fn, ".png")};
if(ttl=="") {ttl=paste0("Voronoi diagram, sites - ", ns, mts)};
cat(" *** Plot file -", pf, "title:", ttl, "\n");
plot(NA, xlim=c(0,m), ylim=c(0,m), xlab="", ylab="", main=ttl);
X=numeric(ns); Y=numeric(ns); C=numeric(ns);
for(i in 1:ns) {
X[i]=sample(0:m1, 1, replace=TRUE);
Y[i]=sample(0:m1, 1, replace=TRUE);
C[i]=randHclr();
}
for(i in 0:m1) {
for(j in 0:m1) {
dm=Metric(m1,m1,mt); k=-1;
for(n in 1:ns) {
d=Metric(X[n]-j,Y[n]-i, mt);
if(d<dm) {dm=d; k=n;}
}
clr=C[k]; segments(j, i, j, i, col=clr);
}
}
points(X, Y, pch = 19, col = "black", bg = "white")
dev.copy(png, filename=pf, width=m, height=m);
dev.off(); graphics.off();
cat(" *** END VD:",date(),"\n");
}
## Executing:
pVoronoiD(150) ## Euclidean metric
pVoronoiD(10,"","",2) ## Manhattan metric
pVoronoiD(10,"","",3) ## Minkovski metric
Output:
> pVoronoiD(150) ## Euclidean metric
*** START VD: Sun Mar 12 19:04:26 2017
*** Plot file - VDR1150.png title: Voronoi diagram, sites - 150
*** END VD: Sun Mar 12 19:11:03 2017
> pVoronoiD(10,"","",2) ## Manhattan metric
*** START VD: Mon Mar 20 13:57:46 2017
*** Plot file - VDR210.png title: Voronoi diagram, sites - 10, mt - 2
*** END VD: Mon Mar 20 13:59:42 2017
> pVoronoiD(10,"","",3) ## Minkovski metric
*** START VD: Mon Mar 20 14:45:15 2017
*** Plot file - VDR310.png title: Voronoi diagram, sites - 10, mt - 3
*** END VD: Mon Mar 20 14:47:21 2017
Racket
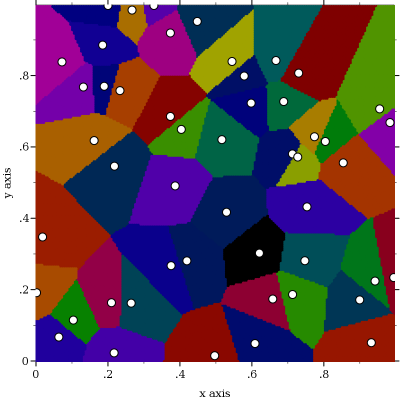
First approach:
#lang racket
(require plot)
;; Performs clustering of points in a grid
;; using the nearest neigbour approach and shows
;; clusters in different colors
(define (plot-Voronoi-diagram point-list)
(define pts
(for*/list ([x (in-range 0 1 0.005)]
[y (in-range 0 1 0.005)])
(vector x y)))
(define clusters (clusterize pts point-list))
(plot
(append
(for/list ([r (in-list clusters)] [i (in-naturals)])
(points (rest r) #:color i #:sym 'fullcircle1))
(list (points point-list #:sym 'fullcircle5 #:fill-color 'white)))))
;; Divides the set of points into clusters
;; using given centroids
(define (clusterize data centroids)
(for*/fold ([res (map list centroids)]) ([x (in-list data)])
(define c (argmin (curryr (metric) x) centroids))
(dict-set res c (cons x (dict-ref res c)))))
Different metrics:
(define (euclidean-distance a b)
(for/sum ([x (in-vector a)] [y (in-vector b)])
(sqr (- x y))))
(define (manhattan-distance a b)
(for/sum ([x (in-vector a)] [y (in-vector b)])
(abs (- x y))))
(define metric (make-parameter euclidean-distance))
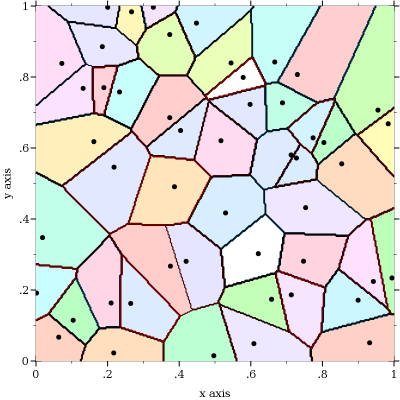
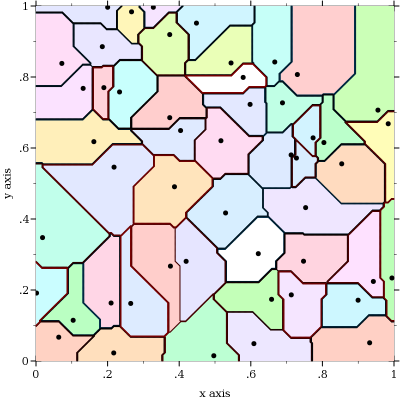
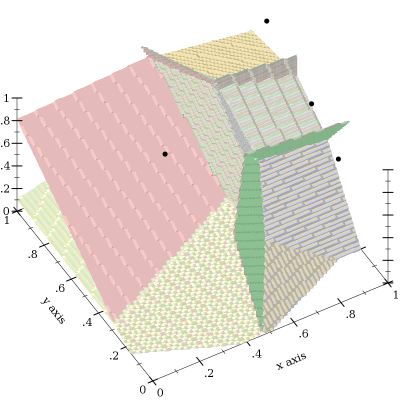
Alternative approach:
;; Plots the Voronoi diagram as a contour plot of
;; the classification function built for a set of points
(define (plot-Voronoi-diagram2 point-list)
(define n (length point-list))
(define F (classification-function point-list))
(plot
(list
(contour-intervals (compose F vector) 0 1 0 1
#:samples 300
#:levels n
#:colors (range n)
#:contour-styles '(solid)
#:alphas '(1))
(points point-list #:sym 'fullcircle3))))
;; For a set of centroids returns a function
;; which finds the index of the centroid nearest
;; to a given point
(define (classification-function centroids)
(define tbl
(for/hash ([p (in-list centroids)] [i (in-naturals)])
(values p i)))
(λ (x)
(hash-ref tbl (argmin (curry (metric) x) centroids))))
Output:
(define pts
(for/list ([i 50]) (vector (random) (random))))
(display (plot-Voronoi-diagram pts))
(display (plot-Voronoi-diagram2 pts))
(parameterize ([metric manhattan-distance])
(display (plot-Voronoi-diagram2 pts)))
;; Using the classification function it is possible to plot Voronoi diagram in 3D.
(define pts3d (for/list ([i 7]) (vector (random) (random) (random))))
(plot3d (list
(isosurfaces3d (compose (classification-function pts3d) vector)
0 1 0 1 0 1
#:line-styles '(transparent)
#:samples 100
#:colors (range 7)
#:alphas '(1))
(points3d pts3d #:sym 'fullcircle3)))
Ring
# Project : Voronoi diagram
load "guilib.ring"
load "stdlib.ring"
paint = null
new qapp
{
spots = 100
leftside = 400
rightside = 400
locx = list(spots)
locy = list(spots)
rgb = newlist(spots,3)
seal = newlist(leftside, rightside)
reach = newlist(leftside, rightside)
win1 = new qwidget() {
setwindowtitle("Voronoi diagram")
setgeometry(100,100,800,600)
label1 = new qlabel(win1) {
setgeometry(10,10,800,600)
settext("")
}
new qpushbutton(win1) {
setgeometry(150,550,100,30)
settext("draw")
setclickevent("draw()")
}
show()
}
exec()
}
func draw
p1 = new qpicture()
color = new qcolor() {
setrgb(0,0,255,255)
}
pen = new qpen() {
setcolor(color)
setwidth(1)
}
paint = new qpainter() {
begin(p1)
setpen(pen)
for i =1 to spots
locx[i] = floor(leftside * randomf())
locy[i] = floor(rightside * randomf())
rgb[i][1] = floor(256 * randomf())
rgb[i][2] = floor(256 * randomf())
rgb[i][3] = floor(256 * randomf())
next
for x = 1 to leftside
for y = 1 to rightside
reach[x][y] = pow((locx[1] - x),2) + pow((locy[1] - y),2)
seal[x][y] = 1
next
next
for i = 2 to spots
for x = locx[i] to 0 step -1
if not (chkpos(i,x,1, rightside-1))
exit
ok
next
for x = locx[i] + 1 to leftside - 1
if not (chkpos(i, x, 1, rightside-1))
exit
ok
next
next
for x = 1 to leftside
for y = 1 to rightside
c1 = rgb[seal[x][y]][1]
c2 = rgb[seal[x][y]][2]
c3 = rgb[seal[x][y]][3]
color = new qcolor() { setrgb(c1,c2,c3,255) }
pen = new qpen() { setcolor(color) setwidth(10) }
setpen(pen)
starty = y
nearest = seal[x][y]
for y = (y + 1) to rightside
if seal[x][y] != nearest
y = y - 1
exit
ok
next
paint.drawline(x,starty,x,y + 1)
next
next
endpaint()
}
label1 { setpicture(p1) show() }
return
func chkpos(site,x,starty,endy)
chkpos = 0
dxsqr = 0
dxsqr = pow((locx[site]- x),2)
for y = starty to endy
dsqr = pow((locy[site] - y),2) + dxsqr
if x <= leftside and y <= leftside and x > 0 and y > 0
if dsqr <= reach[x][y]
reach[x][y] = dsqr
seal[x][y] = site
chkpos = 1
ok
ok
next
return chkpos
func randomf()
decimals(10)
str = "0."
for i = 1 to 10
nr = random(9)
str = str + string(nr)
next
return number(str)
Output image:
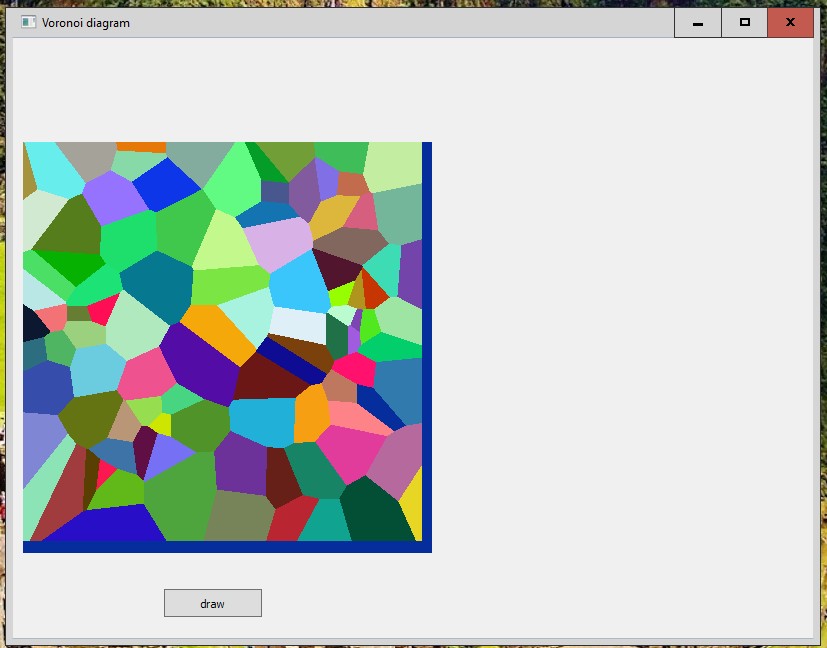
Ruby
Uses [[Raster graphics operations/Ruby]]
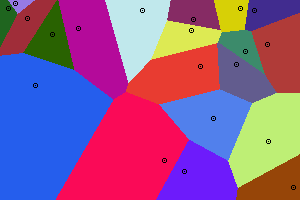
load 'raster_graphics.rb'
class ColourPixel < Pixel
def initialize(x, y, colour)
@colour = colour
super x, y
end
attr_accessor :colour
def distance_to(px, py)
Math::hypot(px - x, py - y)
end
end
width, height = 300, 200
npoints = 20
pixmap = Pixmap.new(width,height)
@bases = npoints.times.collect do |i|
ColourPixel.new(
3+rand(width-6), 3+rand(height-6), # provide a margin to draw a circle
RGBColour.new(rand(256), rand(256), rand(256))
)
end
pixmap.each_pixel do |x, y|
nearest = @bases.min_by {|base| base.distance_to(x, y)}
pixmap[x, y] = nearest.colour
end
@bases.each do |base|
pixmap[base.x, base.y] = RGBColour::BLACK
pixmap.draw_circle(base, 2, RGBColour::BLACK)
end
pixmap.save_as_png("voronoi_rb.png")
Run BASIC
graphic #g, 400,400
#g flush()
spots = 100
leftSide = 400
rightSide = 400
dim locX(spots)
dim locY(spots)
dim rgb(spots,3)
dim seal(leftSide, rightSide)
dim reach(leftSide, rightSide)
for i =1 to spots
locX(i) = int(leftSide * rnd(1))
locY(i) = int(rightSide * rnd(1))
rgb(i,1) = int(256 * rnd(1))
rgb(i,2) = int(256 * rnd(1))
rgb(i,3) = int(256 * rnd(1))
#g color(rgb(i,1),rgb(i,2),rgb(i,3))
#g set(locX(i),locY(i))
next i
#g size(1)
' find reach to the first site
for x = 0 to leftSide - 1
for y = 0 to rightSide - 1
reach(x, y) = (locX(1) - x) ^ 2 + (locY(1) - y) ^ 2
seal(x, y) = 1
next y
next x
#g color("darkblue")
' spots other than 1st spot
for i = 2 to spots
for x = locX(i) to 0 step -1 ' looking left
if not(chkPos(i,x,0, rightSide - 1)) then exit for
next x
for x = locX(i) + 1 to leftSide - 1 ' looking right
if not(chkPos(i, x, 0, rightSide - 1)) then exit for
next x
next i
for x = 0 to leftSide - 1
for y = 0 to rightSide - 1
c1 = rgb(seal(x, y),1)
c2 = rgb(seal(x, y),2)
c3 = rgb(seal(x, y),3)
#g color(c1,c2,c3)
startY = y
nearest = seal(x, y)
for y = y + 1 to rightSide
if seal(x, y) <> nearest then y = y - 1 : exit for
next y
#g line(x,startY,x,y + 1)
next y
next x
#g color("black")
#g size(4)
for i =1 to spots
#g set(locX(i),locY(i))
next i
render #g
end
function chkPos(site, x, startY, endY)
dxSqr = (locX(site) - x) ^ 2
for y = startY to endY
dSqr = (locY(site) - y) ^ 2 + dxSqr
if dSqr <= reach(x, y) then
reach(x,y) = dSqr
seal(x,y) = site
chkPos = 1
end if
next y
end function
Rust
This implementation uses SDL to display the diagram. The actual implementation of the Voronoi diagram is very fast because it's not pixel based, it's vector based, using Fortune's Linesweep algorithm. It can be found in the crate voronoi.
The entire code, including the Crate.toml and a precompiled binary for Windows x86_64, can be found at https://github.com/ctrlcctrlv/interactive-voronoi/
extern crate piston;
extern crate opengl_graphics;
extern crate graphics;
extern crate touch_visualizer;
#[cfg(feature = "include_sdl2")]
extern crate sdl2_window;
extern crate getopts;
extern crate voronoi;
extern crate rand;
use touch_visualizer::TouchVisualizer;
use opengl_graphics::{ GlGraphics, OpenGL };
use graphics::{ Context, Graphics };
use piston::window::{ Window, WindowSettings };
use piston::input::*;
use piston::event_loop::*;
#[cfg(feature = "include_sdl2")]
use sdl2_window::Sdl2Window as AppWindow;
use voronoi::{voronoi, Point, make_polygons};
use rand::Rng;
static DEFAULT_WINDOW_HEIGHT: u32 = 600;
static DEFAULT_WINDOW_WIDTH: u32 = 600;
struct Settings {
lines_only: bool,
random_count: usize
}
fn main() {
let args: Vec<String> = std::env::args().collect();
let mut opts = getopts::Options::new();
opts.optflag("l", "lines_only", "Don't color polygons, just outline them");
opts.optopt("r", "random_count", "On keypress \"R\", put this many random points on-screen", "RANDOMCOUNT");
let matches = opts.parse(&args[1..]).expect("Failed to parse args");
let settings = Settings{
lines_only: matches.opt_present("l"),
random_count: match matches.opt_str("r") {
None => { 50 },
Some(s) => { s.parse().expect("Random count of bad format") }
}
};
event_loop(&settings);
}
fn random_point() -> [f64; 2] {
[rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0., DEFAULT_WINDOW_HEIGHT as f64), rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0., DEFAULT_WINDOW_WIDTH as f64)]
}
fn random_color() -> [f32; 4] {
[rand::random::<f32>(), rand::random::<f32>(), rand::random::<f32>(), 1.0]
}
fn random_voronoi(dots: &mut Vec<[f64;2]>, colors: &mut Vec<[f32;4]>, num: usize) {
dots.clear();
colors.clear();
for _ in 0..num {
dots.push(random_point());
colors.push(random_color());
}
}
fn event_loop(settings: &Settings) {
let opengl = OpenGL::V3_2;
let mut window: AppWindow = WindowSettings::new("Interactive Voronoi", [DEFAULT_WINDOW_HEIGHT, DEFAULT_WINDOW_WIDTH])
.exit_on_esc(true).opengl(opengl).build().unwrap();
let ref mut gl = GlGraphics::new(opengl);
let mut touch_visualizer = TouchVisualizer::new();
let mut events = Events::new(EventSettings::new().lazy(true));
let mut dots = Vec::new();
let mut colors = Vec::new();
let mut mx = 0.0;
let mut my = 0.0;
while let Some(e) = events.next(&mut window) {
touch_visualizer.event(window.size(), &e);
if let Some(button) = e.release_args() {
match button {
Button::Keyboard(key) => {
if key == piston::input::keyboard::Key::N { dots.clear(); colors.clear(); }
if key == piston::input::keyboard::Key::R { random_voronoi(&mut dots, &mut colors, settings.random_count); }
}
Button::Mouse(_) => {
dots.push([mx, my]);
colors.push(random_color());
},
_ => ()
}
};
e.mouse_cursor(|x, y| {
mx = x;
my = y;
});
if let Some(args) = e.render_args() {
gl.draw(args.viewport(), |c, g| {
graphics::clear([1.0; 4], g);
let mut vor_pts = Vec::new();
for d in &dots {
vor_pts.push(Point::new(d[0], d[1]));
}
if vor_pts.len() > 0 {
let vor_diagram = voronoi(vor_pts, DEFAULT_WINDOW_WIDTH as f64);
let vor_polys = make_polygons(&vor_diagram);
for (i, poly) in vor_polys.iter().enumerate() {
if settings.lines_only {
draw_lines_in_polygon(poly, &c, g);
} else {
draw_polygon(poly, &c, g, colors[i]);
}
}
}
for d in &dots {
draw_ellipse(&d, &c, g);
}
});
}
}
}
fn draw_lines_in_polygon<G: Graphics>(
poly: &Vec<Point>,
c: &Context,
g: &mut G,
)
{
let color = [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0];
for i in 0..poly.len()-1 {
graphics::line(
color,
2.0,
[poly[i].x.into(), poly[i].y.into(), poly[i+1].x.into(), poly[i+1].y.into()],
c.transform,
g
)
}
}
fn draw_polygon<G: Graphics>(
poly: &Vec<Point>,
c: &Context,
g: &mut G,
color: [f32; 4]
) {
let mut polygon_points: Vec<[f64; 2]> = Vec::new();
for p in poly {
polygon_points.push([p.x.into(), p.y.into()]);
}
graphics::polygon(
color,
polygon_points.as_slice(),
c.transform,
g
)
}
fn draw_ellipse<G: Graphics>(
cursor: &[f64; 2],
c: &Context,
g: &mut G,
) {
let color = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0];
graphics::ellipse(
color,
graphics::ellipse::circle(cursor[0], cursor[1], 4.0),
c.transform,
g
);
}
Scala
Java Swing Interoperability
Works with Scala 2.13
import java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage
import java.awt.{Color, Graphics, Graphics2D}
import scala.math.sqrt
object Voronoi extends App {
private val (cells, dim) = (100, 1000)
private val rand = new scala.util.Random
private val color = Vector.fill(cells)(rand.nextInt(0x1000000))
private val image = new BufferedImage(dim, dim, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB)
private val g: Graphics2D = image.createGraphics()
private val px = Vector.fill(cells)(rand.nextInt(dim))
private val py = Vector.fill(cells)(rand.nextInt(dim))
for (x <- 0 until dim;
y <- 0 until dim) {
var n = 0
def distance(x1: Int, x2: Int, y1: Int, y2: Int) =
sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2).toDouble) // Euclidian
for (i <- px.indices
if distance(px(i), x, py(i), y) < distance(px(n), x, py(n), y))
n = i
image.setRGB(x, y, color(n))
}
g.setColor(Color.BLACK)
for (i <- px.indices) g.fill(new Ellipse2D.Double(px(i) - 2.5, py(i) - 2.5, 5, 5))
new javax.swing.JFrame("Voronoi Diagram") {
override def paint(g: Graphics): Unit = {g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, this); ()}
setBounds(0, 0, dim, dim)
setDefaultCloseOperation(javax.swing.WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE)
setLocationRelativeTo(null)
setResizable(false)
setVisible(true)
}
}
Seed7
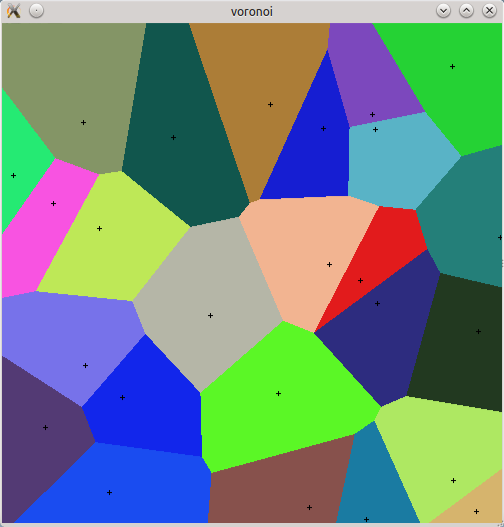
$ include "seed7_05.s7i";
include "draw.s7i";
include "keybd.s7i";
const type: point is new struct
var integer: xPos is 0;
var integer: yPos is 0;
var color: col is black;
end struct;
const proc: generateVoronoiDiagram (in integer: width, in integer: height, in integer: numCells) is func
local
var array point: points is 0 times point.value;
var integer: index is 0;
var integer: x is 0;
var integer: y is 0;
var integer: distSquare is 0;
var integer: minDistSquare is 0;
var integer: indexOfNearest is 0;
begin
screen(width, height);
points := numCells times point.value;
for index range 1 to numCells do
points[index].xPos := rand(0, width);
points[index].yPos := rand(0, height);
points[index].col := color(rand(0, 65535), rand(0, 65535), rand(0, 65535));
end for;
for y range 0 to height do
for x range 0 to width do
minDistSquare := width ** 2 + height ** 2;
for index range 1 to numCells do
distSquare := (points[index].xPos - x) ** 2 + (points[index].yPos - y) ** 2;
if distSquare < minDistSquare then
minDistSquare := distSquare;
indexOfNearest := index;
end if;
end for;
point(x, y, points[indexOfNearest].col);
end for;
end for;
for index range 1 to numCells do
line(points[index].xPos - 2, points[index].yPos, 4, 0, black);
line(points[index].xPos, points[index].yPos - 2, 0, 4, black);
end for;
end func;
const proc: main is func
begin
generateVoronoiDiagram(500, 500, 25);
KEYBOARD := GRAPH_KEYBOARD;
readln(KEYBOARD);
end func;
Original source: http://seed7.sourceforge.net/algorith/graphic.htm#voronoi
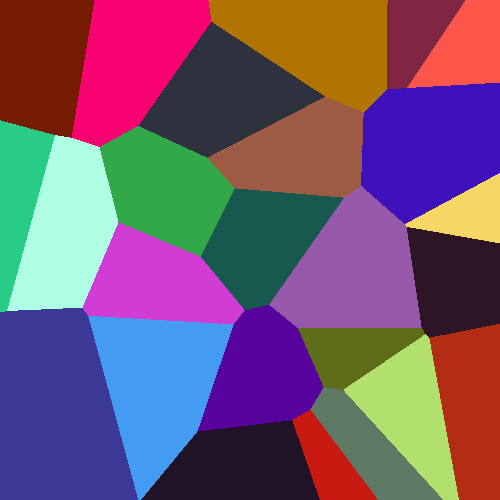
Sidef
Translated from Python.
require('Imager')
func generate_voronoi_diagram(width, height, num_cells) {
var img = %O<Imager>.new(xsize => width, ysize => height)
var (nx,ny,nr,ng,nb) = 5.of { [] }...
for i in (^num_cells) {
nx << rand(^width)
ny << rand(^height)
nr << rand(^256)
ng << rand(^256)
nb << rand(^256)
}
for y=(^height), x=(^width) {
var j = (^num_cells -> min_by {|i| hypot(nx[i]-x, ny[i]-y) })
img.setpixel(x => x, y => y, color => [nr[j], ng[j], nb[j]])
}
return img
}
var img = generate_voronoi_diagram(500, 500, 25)
img.write(file => 'VoronoiDiagram.png')
Output image:

Tcl
package require Tk
proc r to {expr {int(rand()*$to)}}; # Simple helper
proc voronoi {photo pointCount} {
for {set i 0} {$i < $pointCount} {incr i} {
lappend points [r [image width $photo]] [r [image height $photo]]
}
foreach {x y} $points {
lappend colors [format "#%02x%02x%02x" [r 256] [r 256] [r 256]]
}
set initd [expr {[image width $photo] + [image height $photo]}]
for {set i 0} {$i < [image width $photo]} {incr i} {
for {set j 0} {$j < [image height $photo]} {incr j} {
set color black
set d $initd
foreach {x y} $points c $colors {
set h [expr {hypot($x-$i,$y-$j)}]
### Other interesting metrics
#set h [expr {abs($x-$i)+abs($y-$j)}]
#set h [expr {(abs($x-$i)**3+abs($y-$j)**3)**0.3}]
if {$d > $h} {set d $h;set color $c}
}
$photo put $color -to $i $j
}
# To display while generating, uncomment this line and the other one so commented
#if {$i%4==0} {update idletasks}
}
}
# Generate a 600x400 Voronoi diagram with 60 random points
image create photo demo -width 600 -height 400
pack [label .l -image demo]
# To display while generating, uncomment this line and the other one so commented
#update
voronoi demo 60
XPL0

include c:\cxpl\codes; \intrinsic 'code' declarations
def N = 15; \number of sites
int SiteX(N), SiteY(N), \coordinates of sites
Dist2, MinDist2, MinI, \distance squared, and minimums
X, Y, I;
[SetVid($13); \set 320x200x8 graphics
for I:= 0 to N-1 do \create a number of randomly placed sites
[SiteX(I):= Ran(160); SiteY(I):= Ran(100)];
for Y:= 0 to 100-1 do \generate Voronoi diagram
for X:= 0 to 160-1 do \for all points...
[MinDist2:= -1>>1; \find closest site
for I:= 0 to N-1 do
[Dist2:= sq(X-SiteX(I)) + sq(Y-SiteY(I));
if Dist2 < MinDist2 then
[MinDist2:= Dist2; MinI:= I];
];
if MinDist2 then Point(X, Y, MinI+1); \leave center black
];
I:= ChIn(1); \wait for keystroke
SetVid($03); \restore normal text screen
]
Yabasic
clear screen
sites = 200
xEdge = 600
yEdge = 400
open window xEdge, yEdge
dim townX(sites), townY(sites), col$(sites)
for i =1 to sites
townX(i) =int(xEdge *ran(1))
townY(i) =int(yEdge *ran(1))
col$(i) = str$(int(256 * ran(1))) + ", " + str$(int(256 * ran(1))) + ", " + str$(int(256 * ran(1)))
color col$(i)
fill circle townX(i), townY(i), 2
next i
dim nearestIndex(xEdge, yEdge)
dim dist(xEdge, yEdge)
//fill distance table with distances from the first site
for x = 0 to xEdge - 1
for y = 0 to yEdge - 1
dist(x, y) = (townX(1) - x) ^ 2 + (townY(1) - y) ^ 2
nearestIndex(x, y) = 1
next y
next x
color 0,0,255
//for other towns
for i = 2 to sites
//display some progress
//print at(0,20) "computing: ", (i/sites*100) using "###.#", " %"
//look left
for x = townX(i) to 0 step -1
if not(checkRow(i, x,0, yEdge - 1)) break
next x
//look right
for x = townX(i) + 1 to xEdge - 1
if not(checkRow(i, x, 0, yEdge - 1)) break
next x
next i
for x = 0 to xEdge - 1
for y =0 to yEdge - 1
color col$(nearestIndex(x, y))
startY = y
nearest = nearestIndex(x, y)
for y = y + 1 to yEdge
if nearestIndex(x, y) <> nearest then y = y - 1 : break : end if
next y
line x, startY, x, y + 1
next y
next x
color 0,0,0
for i =1 to sites
fill circle townX( i), townY( i), 2
next i
print peek("millisrunning"), " ms"
sub checkRow(site, x, startY, endY)
local dxSquared, y, check
dxSquared = (townX(site) - x) ^ 2
for y = startY to endY
dSquared = (townY(site) - y) ^ 2 + dxSquared
if dSquared <= dist(x, y) then
dist(x, y) = dSquared
nearestIndex(x, y) = site
check = 1
end if
next y
return check
end sub
Translated from Python.
width = 500 : height = 500
open window width, height
export sub hypot(a, b)
return (sqrt(a^2+b^2))
end sub
sub generate_voronoi_diagram(width, height, num_cells)
local nx(num_cells), ny(num_cells), nr(num_cells), ng(num_cells), nb(num_cells)
for i = 1 to num_cells
nx(i) = ran(width)
ny(i) = ran(height)
nr(i) = ran(256)
ng(i) = ran(256)
nb(i) = ran(256)
next
for y = 1 to height
for x = 1 to width
dmin = hypot(width-1, height-1)
j = -1
for i = 1 to num_cells
d = hypot(nx(i)-x, ny(i)-y)
if d < dmin dmin = d : j = i
next
color nr(j), ng(j), ng(j)
dot x, y
next
next
end sub
generate_voronoi_diagram(width, height, 25)
zkl
Uses the PPM class from Bresenham's line algorithm#zkl
Translated from Python.
fcn generate_voronoi_diagram(width,height,num_cells){
image,imgx,imgy:=PPM(width,height),width,height;
nx:=num_cells.pump(List,(0).random.fp(imgx));
ny:=num_cells.pump(List,(0).random.fp(imgy));
nr:=num_cells.pump(List,(0).random.fp(256)); // red
ng:=num_cells.pump(List,(0).random.fp(256)); // blue
nb:=num_cells.pump(List,(0).random.fp(256)); // green
foreach y,x in (imgy,imgx){
dmin:=(imgx-1).toFloat().hypot(imgy-1);
j:=-1;
foreach i in (num_cells){
d:=(nx[i] - x).toFloat().hypot(ny[i] - y);
if(d<dmin) dmin,j = d,i
}
image[x,y]=(nr[j]*0xff00 + ng[j])*0xff00 + nb[j];
}
image
}
generate_voronoi_diagram(500,500,25).write(File("VoronoiDiagram.ppm","wb"));